
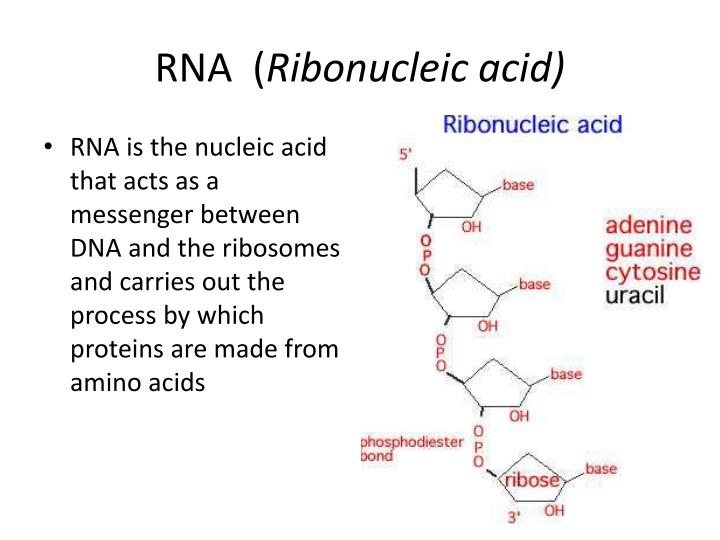
The bases form hydrogen bonds between cytosine and guanine, between adenine and uracil and between guanine and uracil. The phosphate groups have a negative charge each, making RNA a charged molecule (polyanion). A phosphate group is attached to the 3' position of one ribose and the 5' position of the next. Adenine and guanine are purines, cytosine and uracil are pyrimidines. A base is attached to the 1' position, in general, adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), or uracil (U). Hydrogen atoms are not shown.Įach nucleotide in RNA contains a ribose sugar, with carbons numbered 1' through 5'. Main article: Nucleic acid structure Watson-Crick base pairs in a siRNA. For instance, determination of the structure of the ribosome-an RNA-protein complex that catalyzes peptide bond formation-revealed that its active site is composed entirely of RNA. In this fashion, RNAs can achieve chemical catalysis (like enzymes). Unlike DNA, their structures do not consist of long double helices, but rather collections of short helices packed together into structures akin to proteins. Analysis of these RNAs has revealed that they are highly structured. Like DNA, most biologically active RNAs, including mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, snRNAs, and other non-coding RNAs, contain self-complementary sequences that allow parts of the RNA to fold and pair with itself to form double helices.

Ribosomal RNA is in ochre, proteins in blue. This process uses transfer RNA ( tRNA) molecules to deliver amino acids to the ribosome, where ribosomal RNA ( rRNA) then links amino acids together to form coded proteins.Ĭomparison with DNA Three-dimensional representation of the 50S ribosomal subunit. One of these active processes is protein synthesis, a universal function in which RNA molecules direct the synthesis of proteins on ribosomes. Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signals. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA ( mRNA) to convey genetic information (using the nitrogenous bases of guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine, denoted by the letters G, U, A, and C) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides.
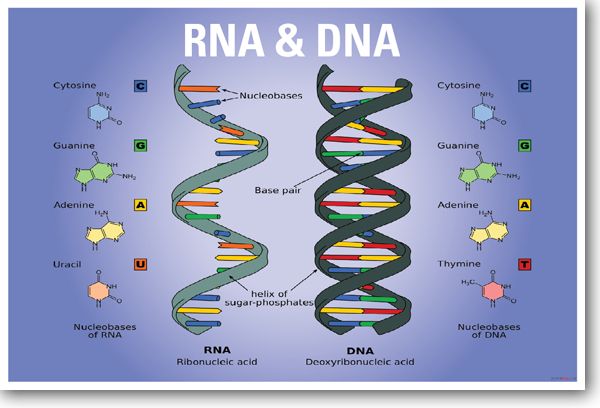
The nucleic acids constitute one of the four major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Ribonucleic acid ( RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself ( Non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for production of proteins ( messenger RNA).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
